UNDERSTANDING
ORAL CANCER
Your Oral Health, Our Priority
INTRODUCTION
ORAL CANCER
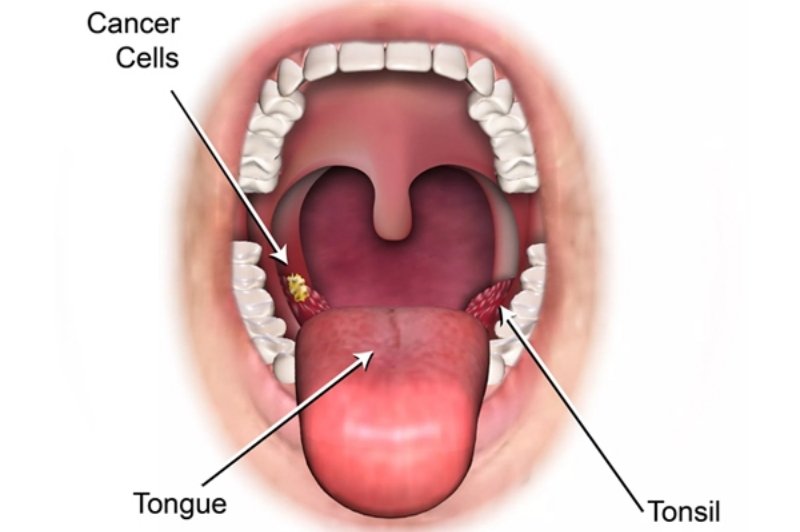
Oral cancer is a disease that results when the cells become abnormal and grow in the mouth, lips, tongue or gums. It can affect daily activities such as speaking, chewing, and swallowing if not treated on time. Early detection plays a vital role in successful treatment and recovery. Oral cancer management nowadays is about curing the disease and enhancing quality of life with modern therapy and a patient-centred approach.
Oral Cancer Facts
- Oral cancer ranks among the top 10 most common cancers worldwide, highlighting the importance of awareness and regular screening.
- Early diagnosis is effective as the survival rate can increase to 80-90 per cent when the disease is caught early.
- The use of tobacco and alcohol can increase the risk by over 15 times, making lifestyle choices a significant factor.
- The incidence of oral cancer in men is almost twice that of women, though cases in women are rising too.
- Routine dental check-ups can easily identify precancerous changes before they develop into high-grade cancer.
ORAL CANCER
Signs & Symptoms
There are warning signs of oral cancer, which one should not disregard. See a specialist if you observe these symptoms for over two weeks.
Constant Mouth Ulcers or Sores
Unhealing mouth ulcers can be one of the early signs of oral cancer.
White or Red Patches in the Mouth
These patches (leukoplakia or erythroplakia) can turn into cancer when not treated.
Pain While Chewing or Swallowing
Difficulty or discomfort during eating may suggest cancerous growth in the oral cavity.
OSMF : Oral Sub - Mucous Fibross
Difficulty in opening the mouth is a common early symptom of OSMF, caused by stiffness and scarring of the inner cheek tissues.
Numbness in the Tongue or Jaw
Loss of sensation in the mouth can signal nerve involvement due to oral cancer.
Lump or Swelling in the Mouth or Neck
A hard lump may represent tumor growth or spread to lymph nodes.
Voice Changes or Difficulty Speaking
Altered speech occur if the cancer affects the tongue, palate, or surrounding tissues.
ORAL CANCER
Causes & Risk Factors
Certain habits, health conditions, and lifestyle factors increase the chances of developing oral cancer.
Tobacco Use (Smoking or Chewing)
This is the greatest risk factor, and it has a significant effect on the chances of getting oral cancer.
Alcohol Consumption (Especially with Tobacco)
The consumption of alcohol, especially in combination with tobacco, increases the risk of cancer.
Poor Oral Hygiene
The persistent irritation of sharp teeth, inappropriate dentures or poor oral health can result in precancerous lesions.
Long Standing trauma
Chronic irritation from sharp tooth or ill fitting dentures.
Low Immunity or Nutritional Deficiencies
A low immune system or vitamin deficiency can predispose an organism.
Family History of Oral or Head & Neck Cancers
Genetic predisposition is also a factor in certain instances.
HPV Infection (Human Papillomavirus)
Some strains of HPV are associated with oral and oropharyngeal cancers.
Complications if Left Untreated
Severe pain & infections
As tumours enlarge and ulcerate, severe pain and infections develop and make the person experience constant discomfort.
Facial disfigurement or loss of oral function
Loss of oral function or disfigurement of the face can be experienced due to the destruction of major structures when tumor growth is uncontrolled.
Cancer spread (metastasis)
Cancer spread (metastasis) to lymph nodes, lungs, or liver, which complicates treatment and increases the difficulty of survival.
Difficulty eating or chewing
Difficulty in eating, chewing, and speaking can severely affect nutrition, communication, and daily life
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the cancer stage, location, and patient’s health.
The primary treatment for most oral cancers, involving tumor removal.
High-energy rays target and kill cancer cells, often used after surgery.
Anti-cancer drugs are given to destroy cancer cells or prevent recurrence.
Advanced therapies that strengthen the immune system or block cancer growth.
Surgical Resection & Reconstruction
Surgery is often the primary treatment for oral cancer, focusing on removing the tumor completely while preserving essential functions like speaking, chewing, and swallowing. Reconstruction restores both function and appearance for a better quality of life.
Wide Local Excision – The tumor and surrounding tissues are removed to ensure complete clearance.
Neck Dissection – Removal of affected lymph nodes if cancer has spread beyond the oral cavity.
Jaw or Tongue Resection – Advanced cases may require partial removal of jawbone, tongue, or palate for full tumor removal.
After resection, reconstruction helps restore function, appearance, and quality of life.
Local Flap Reconstruction – Uses tissue from inside the mouth or cheek to close small defects, offering faster recovery.
Regional Flap Reconstruction – Tissue from nearby areas like the neck or chest is rotated to cover larger defects effectively.
Free Flap Reconstruction (Microvascular Surgery) – Tissue with its blood supply from distant sites (thigh, forearm, leg) is transplanted, ensuring the best functional and cosmetic outcomes in major surgeries.
Speech Therapy – Helps regain clear communication after tongue or palate surgeries.
Nutritional Guidance – Dieticians provide support for safe swallowing and healthy recovery.
Physiotherapy – Maintains mobility and flexibility in the jaw and neck after surgery.
Emotional Support – Counseling and support groups help patients cope with anxiety, depression, and social confidence.
Why To Consult Dr. natasha

