PARATHYROID TUMORS TUMORS TUMORS
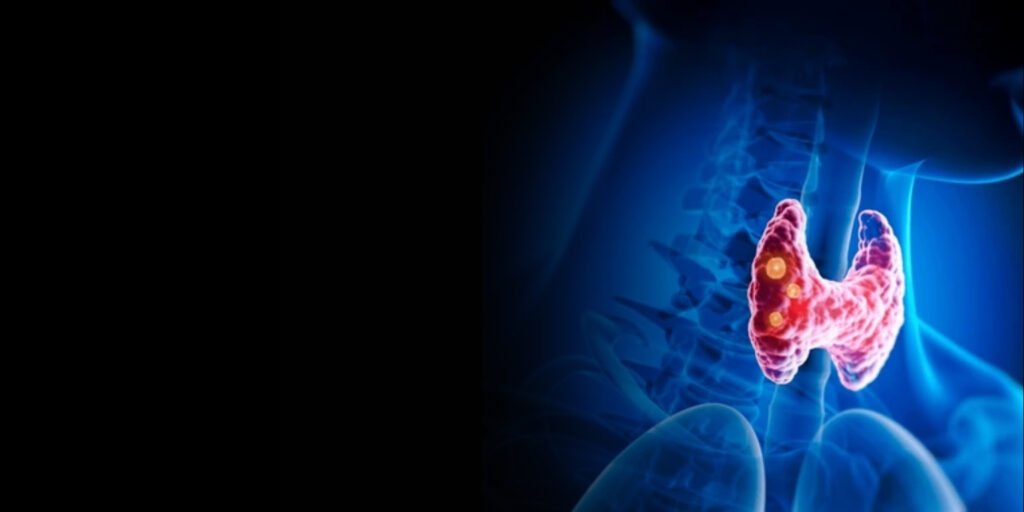
PARATHYROID TUMOR TUMOR TUMOR
What is PARATHYROID TUMORS?
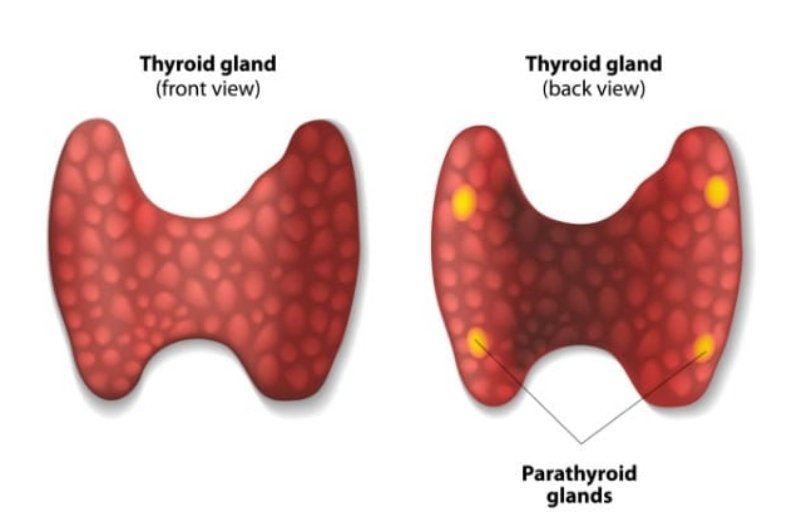
Parathyroid tumors are abnormal growths in the tiny parathyroid glands behind the thyroid. These glands regulate the calcium level in the body using parathyroid hormone (PTH). Tumors - usually benign but sometimes cancerous - can cause overproduction of PTH, leading to dangerously high calcium levels (hyperparathyroidism) and complications affecting bones, kidneys, and overall health.
Parathyroid tumors are abnormal growths in the tiny parathyroid glands behind the thyroid. These glands regulate the calcium level in the body using parathyroid hormone (PTH). Tumors - usually benign but sometimes cancerous - can cause overproduction of PTH, leading to dangerously high calcium levels (hyperparathyroidism) and complications affecting bones, kidneys, and overall health.
PARATHYROID TUMOURS
Signs & Symptoms
Parathyroid tumors usually affect hormone production, leading to calcium imbalances in the body. Early detection helps prevent serious complications.
Kidney Stones
Calcium deposits in the kidneys may cause pain, urinary dysfunction or frequent stones.
Bone Pain & Weakness
Parathyroid hormones can make bones fragile and joints painful.
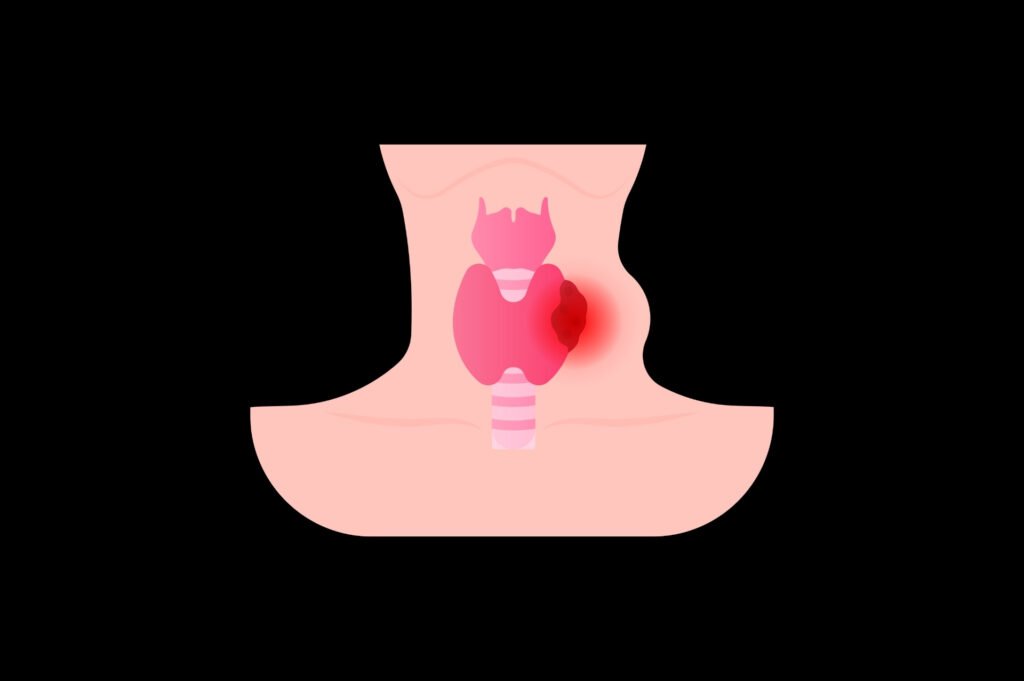
Neck Lump
A slight enlargement can sometimes be experienced lower on the neck or thyroid region
Elevated Blood Calcium Levels (Hypercalcemia)
Calcium can cause exhaustion, nausea, and frequent urination.
Abdominal Pain & Digestive Issues
Calcium imbalance may cause nausea and vomiting, constipation or loss of appetite
Cognitive Symptoms
With long-term high levels of calcium, confusion, memory problems or depression may occur.
PARATHYROID TUMOURS
CAUSES & RISK FACTORS
Parathyroid tumors are mostly linked to hormonal and genetic factors, though lifestyle and medical conditions can contribute.
Radiation Exposure to Neck
The radiation therapy of the past may predispose to tumours.
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
The most typical cause of parathyroid tumours is overactivity of the parathyroid glands.
Genetic Mutations & Family History
Conditions such as MEN1 or MEN2 syndromes may predispose a person to parathyroid tumours.
Age & Gender
It is more common in individuals above 50 and a little more common among women.
Chronic Kidney Disease
The chronic kidney problems can trigger secondary parathyroid enlargement.
Vitamin D Deficiency
Low vitamin D may cause excess activity of the parathyroid glands.
Treatment Options
Parathyroidectomy (Focused/MIRP)
Bilateral Neck Exploration
Auto Transplantation
Lymph Node Dissection
Calcium & Hormone Monitoring
Treatment Options
Parathyroidectomy (Focused/MIRP)
Bilateral Neck Exploration
Auto Transplantation
Lymph Node Dissection
Calcium & Hormone Monitoring
Surgical Resection & Reconstruction
Surgery is the primary and most effective treatment for parathyroid tumors, particularly in cases of parathyroid adenoma, hyperplasia, or carcinoma. The main goal is to remove the diseased gland while preserving healthy parathyroid tissue and maintaining normal calcium balance.
Focused Parathyroidectomy – A minimally invasive approach where only the abnormal gland identified on scans is removed, often done through a small incision.
Bilateral Neck Exploration – When imaging is unclear, surgeons explore all four glands to identify and remove diseased ones while preserving normal glands.
Parathyroid Carcinoma Resection – For malignant tumors, a more extensive surgery may be required, sometimes including removal of part of the thyroid gland and nearby tissues to ensure complete clearance.
Re-exploration Surgery – In cases of recurrent or persistent hyperparathyroidism, revision surgery may be needed with advanced intraoperative guidance.
Since parathyroid tumors generally do not cause large structural defects like oral or salivary cancers, reconstruction focuses on functional preservation rather than cosmetic repair:
Parathyroid Autotransplantation – A portion of healthy parathyroid tissue may be transplanted into the neck muscle or forearm to maintain calcium regulation after tumor removal.
Local Tissue Adjustment – Small repairs may be made to surrounding soft tissues, muscles, or thyroid structures if they are partially removed during surgery.
Nerve Preservation & Repair – Special care is taken to protect the recurrent laryngeal nerve to maintain normal voice; if injured, nerve grafting or voice therapy may be required.
Calcium & Vitamin D Management – Patients may require temporary supplementation until the remaining glands function normally.
Voice & Swallowing Support – If the recurrent laryngeal nerve is affected, speech therapy helps restore voice and swallowing.
Regular Monitoring – Long-term follow-up with calcium and PTH (parathyroid hormone) levels ensures stable recovery and prevents recurrence.
Emotional Well-being – Since hormonal disorders can affect mood, energy, and confidence, supportive care and counseling play an important role in holistic recovery.
Why To Consult Dr. Natasha Lalwani?
Parathyroid tumors may be small, but their effects on your body can be huge. Timely surgery not only protects your bones, kidneys, and heart - it restores your energy and quality of life.
~ DR. NATASHA LALWANI
Parathyroid tumors may be small, but their effects on your body can be huge. Timely surgery not only protects your bones, kidneys, and heart - it restores your energy and quality of life.
~ DR. NATASHA LALWANI
Experiencing High Calcium–Related Symptoms?
get evaluated today.
Book your consultation with Dr. Natasha for expert parathyroid care.

